Audit Walkthrough
- Audit Workflow
- File Setup
- Planning and Risk Assessment
- Risk Response
- Completing and Reporting
- Constellations
Audit Workflow
This walkthrough provides an overview on the features and essentials to get you started with working with Audit. It is based on the following logical user workflow diagram below.
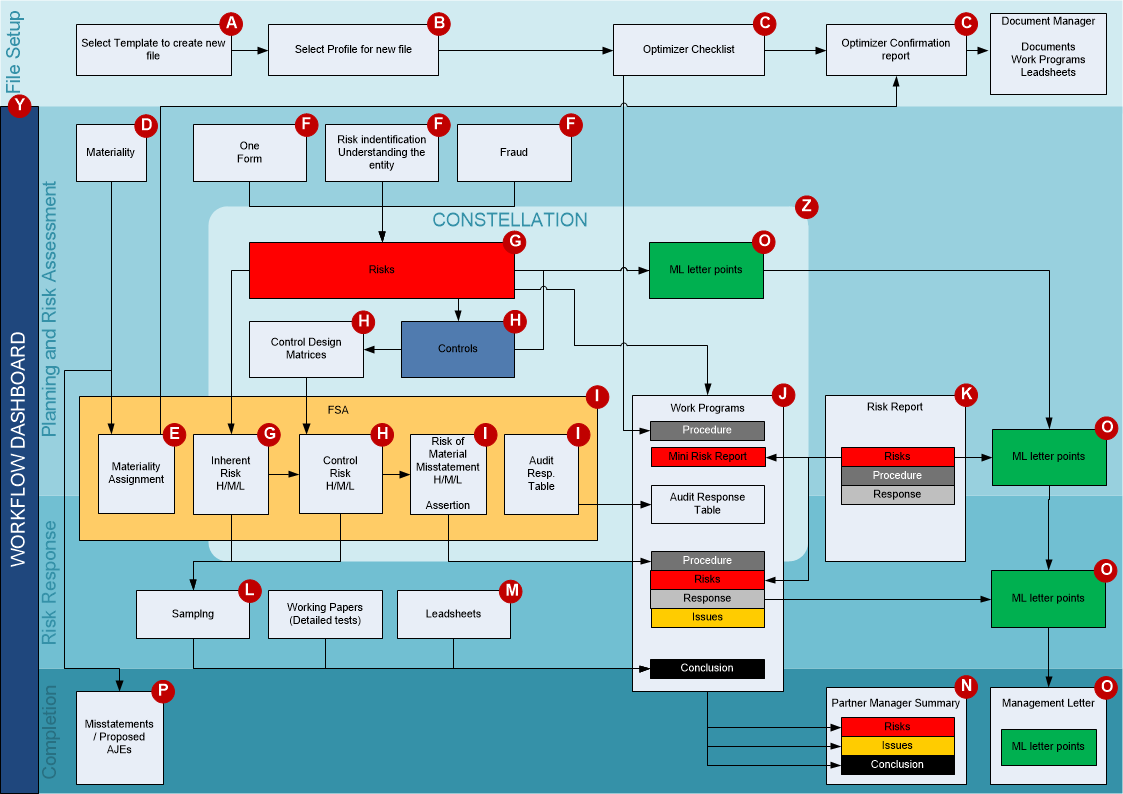
File Setup
A - Select Template to create a New File
Users can select the template to base each new engagement file on when they are creating the engagement file. The new engagement file is a one-to-one copy of the master template. For more information, see Creating Client Files
B- Select Profile for New File
After creation of the engagement file, users are automatically prompted to select a profile for the engagement file. By selecting a profile irrelevant documents are deleted and relevant settings are loaded.
After the profile selection, users are presented with an "Optimiser checklist" specific to the selected profile.
For more information, see Completing Client File Setup.
C- Optimiser Checklist
After the profile selection, users are presented with an "Optimiser checklist" specific to the selected profile. For more information on this, see Optimiser Checklist.
Y- Dashboard
The workflow dashboard is designed to offer an easy way to navigate the engagement. It breaks the audit engagement up into three main parts:
- Planning and Risk Assessment
- Risk Response
- Completing and Reporting
Within these main parts the overall steps are shown and clicking a step will show the documents relevant for that step. As the engagement progresses and documents are completed the steps in the dashboard will be marked as completed as well, providing a high level progress view.
Planning and Risk Assessment
D - Materiality
In the materiality document balances are automatically brought in from the Working Papers trial balance. The following materiality amounts can be calculated from the trial balance amounts and defined for the engagement:
- Overall materiality
- Performance materiality
- Adjusted performance materiality per FSA
- Specific materiality amounts
For all materiality amounts both preliminary and final values can be documented. For more information, see Materiality.
E- Materiality Assessment
After calculation of the materiality the Financial Statement Areas Worksheet automatically selects which FSAs are material based on balances. Users can override the materiality assignment based on professional judgement. User overrides are clearly shown.
Audit will suggest the deletion of complete audit sections for immaterial FSAs.
F - Planning Documentation
Flat forms
Flat forms are CaseView documents with limited automation and can be compared to an automated combination of a text document and a spreadsheet. Examples of flat forms are OneForm and Understanding the Entity. Access to CaseView design mode can be granted allowing full customization. All the key information inputted into flat forms is stored in databases, eliminating the risk of losing information during updates.
Checklists
Checklists are a critical component of Audit. Checklists contain procedures to address the engagement as a whole and for the planning, risk assessment, risk response and completion phases of the engagement. Checklists has its own procedure library. Procedures can be set to be required for all engagements.
For more information, see Checklists.
G - Risks
Risks are stored in the database using the risk dialog as the interface. Through the risk dialog, risks can be linked to other components in Audit and linked objects can be easily navigated and modified. All risks can be set to be rolled forward to the to the next years engagement file.
The main attributes for risks are:
- Significant risk.
- Assessment of the level of inherent risk (IR), control risk (CR), risk of material misstatement (RMM).
- Link to one or more FSAs, Business cycles, Controls, Reportable Items, Audit programs and procedures.
- Narratives for "Management response" and "Audit response".
Risk information is automatically transferred and used in the following:
- FSA, identified risks are shown on the FSA the risks are linked to.
- Risks will show at the relevant assertion line, when all assertions are shown in detail.
- The risk assessment values of identified risks populate the risk at the assertion level in the FSA. Depending on the profile configuration this can be the either the IR or the RMM.
- The risk report shows all of the properties of all risks identified. For procedures linked to a risk, the completion response of the procedures is also shown.
- Work program - at the top in the "mini risk report", showing risks that are addressed in each work program.
- Checklists - at the top in the "mini risk report", showing which risks are identified through this checklist.
- "Partner Manager Summary document" - The control design matrix for the business cycle to which the risk is linked, so it clearly shows which controls mitigate which risks.
- Reportable items report - indicates which risks have been reported on in letters like the management letter.
- Caseware Constellation - risks are a key element of Constellation, providing views that allow users to easily see if a risk has been mitigated by controls and or responded to sufficiently through audit procedures.
- Caseware Q - the total number of risks and significant risks identified is published to Q.
H- Controls
Controls are stored in the database using the controls dialog as the interface. Through the controls dialog controls can be linked to other components in audit and linked objects can be easily navigated and modified. All controls can be set to be rolled forward to the next years engagement file.
The main attributes for controls are:
- Key control
- Results of the "Design and im of the control environment"
- Results of the "Tests of control"
- Link to one or more Business cycles, Risks, Reportable Items, Control environment evaluation supporting work papers, Test of controls supporting work papers.
Controls information is automatically transferred and used in the following:
- Control design matrix, in each matrix (per business cycle) all linked controls are shown as rows and all linked risks as columns, providing a clear overview of which risks are mitigated by which controls.
- The control design matrix can be filtered on risk assertions, clearly showing the information needed by users to form a conclusion on the CR per assertion.
- FSA, the CR assessment can be populated from the conclusions per assertion in the "control design matrix".
- The reportable items report, so it shows which controls have been reported on in letters like the management letter.
- Caseware Constellation, controls are a key element of Constellation.
- Caseware Q, the total number of controls and key controls is published to Q.
I - FSA - Planning and Risk Assessment
The FSA worksheet is the central component of Audit. In the FSA information from many other components is bundled and the FSA drives the behaviour of other components. Each line shows the FSA and its balances from the Working Papers trial balance. The FSA worksheet can be grouped by individual account or audit area.
In the FSA worksheet users make the following key decisions, supported by built in automation based on information from other components:
- Which FSA is material, based on information from the materiality calculation.
- Differences in materiality between planning and final balances or materiality calculations can generate warnings indicating possible over or under auditing.
- Adjusted performance materiality amounts will show at the relevant FSA.
- Manual overriding of materiality suggestions are indicated by override indicators (red dots).
- Risk assessment per FSA at the assertion level
Inherent risk can be populated from the assessment of linked specific risks.
Control risk can be populated from the control design matrix for each business cycle.
Risk of Material Misstatement (RMM) can be calculated from the values set for inherent risk and control risk, based on business rules set per profile. These rules can be set by the firm.
- The risk assessment can be signed off per assertion.
- Manual overriding of suggested risk assessment level are indicated by red borders.
- Risk response (optional)
- Selection of the type of procedures.
For more information on the FSA, see FSA.
Risk Response
J- Work Programs
Audit can be configured in two ways:
1. Default work program procedures
The default work program contains the default procedures (substantive - basic) and based on risks identified and risk assessment at the assertion level procedures are inserted or deleted:
- users will select the relevant assertions in the FSA. Upon opening the work program the procedures linked to only irrelevant assertions will be automatically deleted.
- users will set the level or RMM (H, M, L) per assertion in the FSA. Upon opening the work program procedures will be automatically included or deleted based on the level of risk they are assigned to:
- Applicable if RMM is larger than Low (always applicable if assertion is relevant).
- Applicable if RMM is larger than Medium.
- Applicable if RMM is High.
- Upon opening the work program procedures linked to a risk will be inserted automatically.
2. "Blank sheet approach"
The default work program is empty, all procedures are in the procedure library, and procedures are automatically inserted based on risks identified and risk assessment at the assertion level.
- users will select the relevant assertions in the FSA. Upon opening the work program the procedures linked to the relevant assertions will be automatically included.
- users will set the level or RMM (H, M, L) per assertion in the FSA. Upon opening the work program procedures will be automatically included based on the level of risk they are assigned to:
- Applicable if RMM is larger than Low (always applicable if assertion is relevant).
- Applicable if RMM is larger than Medium.
- Applicable if RMM is High.
- Upon opening the work program procedures linked to a risk will be inserted automatically.
L, M - Leadsheets and Sampling
Automatic documents are documents that generate and display specific Working Papers data based on the format and setting selected. There are over twenty five different types of automatic documents including leadsheets, analytical review and account analysis. Automatic documents contain real-time linkages from the trial balance and engagement properties.
Sampling forms allow the auditor to document the use of statistical or non-statistical (judgmental) sampling. The assessment level set for inherent risk and control risk flows into the sampling forms from the FSA.
K - Risk Report
In the risk report all the properties of all risks identified are shown. Different views can be created and saved by both the firm and/or at the engagement level, enabling users to see the required information in various combinations. An important view is the combination of the risk assessment at the FSA and assertion level combined with the specific risks.
Completing and Reporting
O - Reportable Items
Reportable items (e.g. management letter points) are stored in the database using the reportable items dialog as the interface. Through the reportable items dialog, reportable items can be linked to other components in audit and linked objects can be easily navigated and modified. Reportable items are summarized and can automatically be transferred to reporting letters including those to management and those charged with governance. All reportable items and linked recommendations can be set to be rolled forward to the next year's engagement file.
The main attributes for reportable items are:
- Recommendation, multiple recommendations can be documented per reportable item.
- Management response.
- Link to one or more Risks, Controls, Source documents.
N - Misstatements
The Summary of Identified Misstatements document provides the auditor with the effect of total identified misstatements on the audit and provide drill down to the individual misstatements.
P - Partner Manager Summary
The Partner and Manager Summary Report summarizes key information from the engagement file. This summary assists reviewers by consolidating key information and issues in the audit in one document for review. Drill down is available if more detail is required.
Z- Constellation
Constellation enables users to visualize the relationships between key elements that have been identified in an audit engagement. By using various views of the data, all members of an audit engagement team can review the critical data.
The traditional form based approach to documenting key relationships and critical issues in an audit engagement is very difficult for both new staff on an engagement and new members of the profession. Constellation's powerful visualization helps new members of the engagement team quickly understand the critical audit issues in an engagement and results in both a better training for the staff and a better audit. All views in Caseware Constellation are generated from the same database as the audit documentation, ensuring they are always consistent and up to date.
For more information, see Constellation.
