Creating and Administering Knowledge Library Content
Building the Knowledge Library file
In CaseView, you can create a new Knowledge Library file on the File tab, click Knowledge Library, and then click New Knowledge Library.
Library content entries are stored in documents which obey the same rules as typical CaseView documents. There is no limit to the number of library documents that can be created, or the amount of content contained within. It is not necessary to create a new library document for each piece of content. A single library document could hold any number of linkable content segments, such as various versions of the Notice to Reader.
More attention to protection and security should be considered when dealing with libraries. Changes made to the content of the library have the potential to affect a large number of live client files. Write access to the library should be limited to the library creators/administrators.
To apply password protection to Design Mode click Lock/Unlock on the Home tab and enter a password twice.
Generating Library Content
Begin generating library content in the newly created document. The feature set in a Knowledge Library document is not restricted; Libraries can include tables, graphs, images, etc. The Library document can also include structural content such as customized headers and footers.
Notes
- Header and footer Library content must be built in the body of the library itself in the same way other Knowledge Library content is generated, not by going into the Document | Attach screen. Even if it is labelled correctly, content built outside the main body of the library will not be recognized as linkable content in a CaseView document. This includes Headers/Footers, Carry Forward Headers, and Freezes.
- In a destination CaseView document, these areas outside the main body of the document can accept Knowledge Library links in the same way body content does. There are no restrictions in that regard.
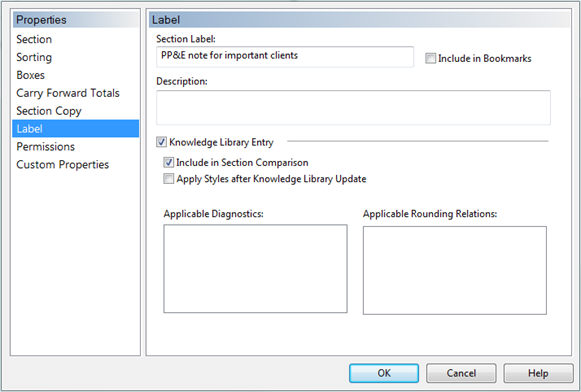
Once created, each library content entry is then flagged.
- Select the portion of the Knowledge Library document you want to assign a flag to.
-
On the Home tab, click Section.
-
Under Available Sections, select the section you want to modify and click Modify.
-
Click the Label tab.
-
In the Section Label box, enter a name for the section.
-
In the Description box, enter a detailed description for the section.
- Select the Knowledge Library Entry option.
- If applicable, select the Include in section comparison option to include the current section when performing comparison and revision.
- If desired, select the Apply styles after Knowledge Library update option to reapply the style to the section after updating. With this option selected, Working Papers/Time will not take the paragraph formatting into consideration when performing a comparison.
- If diagnostics are loaded into the document, select the diagnostics applicable to the section under Applicable Diagnostics.
Saving the Knowledge Library
Once the content has been built, click File | Save. A prompt will appear asking if this document should be added to a Knowledge Library Index. Please refer to the help topic About the Knowledge Library Index for more information about this option.
If not making use of an Index, save the library to a central location where staff have at least Read access.
Opening a Knowledge Library document
- On the File tab, click Knowledge Library, and then click Open Knowledge Library.
- Select the Knowledge Library document to open and then click Open. When the library opens, linked cells populate with data from the active database, if applicable.
Notes
-
When saving changes in a Knowledge Library that is linked to a Knowledge Library Index, a prompt will appear to log into the index.
If the file is not currently linked to an existing Index, CaseView asks if it should be linked. Click No if the library document should remain autonomous.




